Content API
Getting Started
Installing
npm i @bageldb/bagel-db
yarn add @bageldb/bagel-db
pnpm add @bageldb/bagel-db
1. Add BagelDB to your pubspec.yaml file:
bagel_db:
2. Run the command:
flutter pub get
2
3
4
Importing
import Bagel from '@bageldb/bagel-db';
// or
const Bagel = require('@bageldb/bagel-db');
2
3
4
5
<!-- or for cdn version -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@bageldb/bagel-db"></script>
2
import 'package:bagel_db/bagel_db.dart';
Initialize
let API_TOKEN = 'AUTH_TOKEN';
let db = new Bagel(API_TOKEN);
2
String apiToken = "AUTH_TOKEN"
BagelDB db = BagelDB(token: apiToken);
2
Get Collection
Retrieve multiple items from a collection
- By default, this will return the first 100 items in the collection, in order to get a specific set of items see below in Pagination
- Nested collection fields will not be retrieved unless they are specifically projected on using the
projectOnfeature (see below)
db.collection('articles').get();
db.collection("articles").get()
Note: 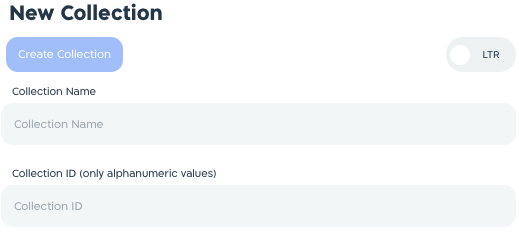
**Collection Name** is for internal use only.
Use the automatically generated **Collection ID** (case sensitive) :::
For a nested collection, item() and collection() can be chained till the correct collection and item is reached
db.collection('books').item('sds232323d').collection('reviews').get();
db.collection("articles").item("sds232323d").collection("reviews").get()
Pagination
BagelDB has built in pagination, you can set the number of items per page and the page you would like to retreive
db.collection('articles').perPage(50).pageNumber(2).get();
db.collection("articles").perPage(50).pageNumber(2).get()
2
Projection
It is possible to project on and project off for all fields in an item, enabling you to retrieve only exactly what is required in the response body
- It is not possible to mix both projectOn and projectOff
- Metadata field will always be retrieved unless explicitly projectedOff i.e _id, _lastUpdateDate and _createdDate
db.collection("articles").projectOn("title,name").get()
<--- OR ---->
db.collection("articles").projectOff("title,name").get()
2
3
Querying
Multiple forms of querying are available:
- Equals Operator "="
- Not Equals Operator "!="
- Greater Than Operator ">"
- Less Than Operator "<"
- Regex Operator "regex"
- GeoPoint Within Operator "within"
Method: query(key, operator, value)
db.collection('books').query('name', '=', 'Of Mice and Men').get();
db.collection('books').query('bookName', '!=', 'Of Mice and Men').get();
2
3
db.collection("books").query("name", "=", "Of Mice and Men").get()
db.collection("books").query("bookName","!=", "Of Mice and Men").get()
2
3
Special Cases:
Item Reference field
An itemRef field expects to get a field name, operator, and comma separated values of one or more of the ids of the relevant referenced items. It will return one of any of the values provided
db.collection('books').query('author.itemRefID', '=', '5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05,5ed9a0a573c14625ry830v52').get();
db.collection("books").query("author.itemRefID", "=", "5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05,5ed9a0a573c14625ry830v52").get()
2
The expected return for the above query are the list of books by either author ids provided. It will also return the books where the author is only one of many authors of that book.
The same applies for not operation :!=: where the expected return is to get all the items, that do not have any of the references provided
db.collection('books').query('author.itemRefID', '!=', '5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05,5ed9a0a573c14625ry830v52').get();
db.collection("books").query("author.itemRefID","!=","5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05,5ed9a0a573c14625ry830v52").get()
The expected response for the above query is all the books that do not contain any of the id's of the provided values. It will not return even where there are other authors to that book.
GeoPoint field
A Geo Point field can be queried if it lies within X radius from another Geo Point.
For example, to query for any hotel within 800 meters of the point 31.75494235983889, 35.214322441328519, the following would be used:
db.collection('hotels')
.query('location', BagelDB.WITHIN, BagelDB.GeoPointQuery(31.75494235983886, 35.214322441328534, 800))
.get();
2
3
Get a Single Item
db.collection('articles').item('5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05').get();
//or for a nested item
db.collection('books').item('sds232323d').collection('reviews').item('232323323').get();
2
3
db.collection("articles").item("5e89a0a573c14625b8850a05").get()
Create Item
db.collection('articles').post({ YOUR_OBJECT });
db.collection("articles").post({YOUR_OBJECT})
Note:
Name is for internal use only.
Use the automatically generated Slug (case sensitive) 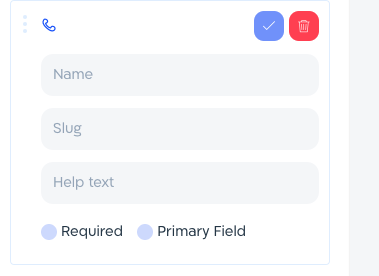
expected response
{
"id": "ITEM_ID"
}
2
3
Set Item ID
When creating an item the _id will be set for you by the server. If you require to set the _id of the item, use the set method:
db.collection('articles').item('YOUR_ITEM_ID').set({ OBJECT_CHANGES });
If the _id is not unique the server will throw an error
Update Item
db.collection('articles').item('ITEM_ID').put({ OBJECT_CHANGES });
db.collection("articles").item("ITEM_ID").put({OBJECT_CHANGES})
expected response
{
"id": "ITEM_ID"
}
2
3
Update Reference Field
It is possible to also update a specific reference field
db.collection('articles').item('ITEM_ID').append('FIELD_SLUG', 'ITEM_REF_ID');
It is also possible to remove one item reference from a reference field
db.collection('articles').item('ITEM_ID').unset('FIELD_SLUG', 'ITEM_REF_ID');
Delete Item
Will delete the entire item for good.
db.collection('articles').item('ITEM_ID').delete();
Uploading asset
Method Signature: uploadImage(imageSlug, {selectedImage, imageLink, altText})
selectedImage expects a file stream i.e fs.createReadStream(filename) OR a blob
imageLink can be a link to a file stored somewhere on the web
The method checks if imageLink exists and if not will use selectedImage
The request is sent via a FormData request.
let image = {
selectedImage: fs.createReadStream('/foo/bar.jpg'),
altText: 'johnny',
};
db.collection('users').item('3423432').uploadImage('profilePic', image);
//OR
let image = {
imageLink: 'https://example.com/image.jpg',
altText: 'johnny',
};
db.collection('users').item('3423432').uploadImage('profilePic', image);
//OR
let image = {
imageLink: 'https://example.com/image.jpg',
altText: 'johnny',
};
db.collection('users').item('3423432').uploadImage('profilePic', image);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
File image = File('/Users/userName/Desktop/photo-test.jpeg');
db.collection("users").item("3423432").uploadImage("profilePic", image)
2
Live Data
See live concepts for more details about how live data works, and the form of the message received.
In the JS library, the listen method takes two call-backs. The first is the onMessage function, which listen calls when it received a new message, inserting a Message Event. From there you can use the message event as required extracting out the message data. The data will be under event.data in a stringified json format. The second callback is the onError callback; when the listener encounters an error it calls the onError callback with error.
Listen only returns events that occurred after the listen has been called. In order to get items that have occurred before the listen is called, a separate get request is required.
If it appears that listening is not connecting, check that the API token has read access on the collection being listened to.
let messages = [];
let onMessageEvent = (event) => {
let eventData = JSON.parse(event.data);
let messageItem = eventData.item;
messages.push(messageItem);
};
db.collection('messages').listen(onMessageEvent);
2
3
4
5
6
7
db.collection("messages").listen((event) => {
print(event)
});
2
3
Bagel User with Items
View Bagel Users
To view the bagel users associated with an item.
db.collection('books').item('ITEM_ID').users();
Expected Response
[{ "userID": "213-3213c-123c123-1232133" }]
Add a Bagel User
In order to add the api token must have User Admin permissions, it is suggested to only use this token server side To add a Bagel User to an item
db.collection('books').item('ITEM_ID').addUser('USER_ID');
Remove a Bagel User
In order to remove the api token must have User Admin permissions, it is suggested to only use this token server side
To remove a Bagel User from an item
db.collection('books').item('ITEM_ID').removeUser('USER_ID');
Version 0.3.38 onwards
Querying Collections with MongoDB "find" and "aggregate"
Starting from version 0.3.38, the REST API supports querying collections based on MongoDB's "find" and "aggregate" operations. This allows for more flexible and powerful data retrieval.
Aggregation Pipeline
To perform an aggregation using the REST API, you can use the following endpoint:
https://api.bagelstudio.co/api/public/collection/{{collectionID}}/items?aggregationPipeline=[{"$match":{"_id":{"$ne":"63a491f7ea55eccfb7b1f3f3"}}},{"$sort":{"firstName":1}},{"$skip":0},{"$limit":1}]
You can specify the aggregation pipeline as a query parameter, aggregationPipeline, which should be an array of aggregation stages. Each stage is defined using MongoDB's aggregation syntax. In the example above, the pipeline includes $match, $sort, $skip, and $limit stages.
Find Method
The find method can be used both via the REST API and the SDK. The syntax is similar to MongoDB's "find" operation. Here are some examples:
// SDK Example
db.collection('slug').find({ 'products.name': 'Product 1' });
2
// REST API Example
https://api.bagelstudio.co/api/public/collection/{{collectionID}}/items?find={"products.name":"Product 1"}
2
Date Queries
When querying by date, there are specific formats to follow. Here are some examples:
// SDK Example
db.collection('posts')
.find({
authorName: 'John',
dateField: 'Date(2022-02-22)',
nestedCollection: {
$elemMatch: {
nestedField: 'nestedValue',
},
},
})
.get();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// SDK Example
const { data } = await db
.collection('posts')
.find({
groups: {
$elemMatch: {
isClosed: false,
},
},
})
.get();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
In the first example, the date field is specified using the format "Date(YYYY-MM-DD)". The second example demonstrates querying a nested collection using $elemMatch.
Please note that these examples are provided to showcase the usage of querying collections with MongoDB's "find" and "aggregate" operations. Adjustments might be required based on your specific implementation and requirements.
